In the robotics world, the design of the intake mechanism is paramount, determining how efficiently a robot can pick up, hold, and release objects. As robots tackle diverse challenges—from competitions to real-world applications—it’s crucial to understand the various intake designs available. Here, we’ll delve into three popular intake designs, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages to assist you in making an informed decision based on the task at hand for which intake would be most optimal.
- Horizontal Roller Intake
- Advantages:
- Due to the object being trapped between two rollers, it can accommodate objects of various shapes without needing precise alignment.
- The design allows for both pick-up and release of objects with equal ease by just reversing the roller direction.
- Disadvantages:
- The intake width might restrict the size of objects it can capture effectively.
- Requires synchronization between the two rollers, leading to potential mechanical and programming complexities.
- Advantages:
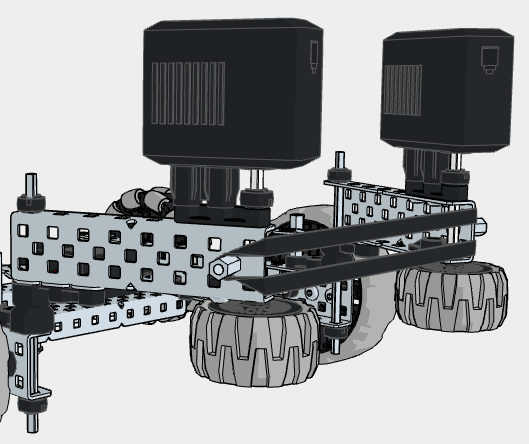
Below is an example of the horizontal roller intake utilizing 5.5W Smart Motors. You’ll find the horizontal intake located at the front of the robot, which includes two horizontal wheels primed to intake objects at varying sizes. A key design feature to this example is the floating intake, which allows for greater adaptability to intaking various objects at different sizes.
- Vertical Roller Intake
- Advantages:
- Since it primarily uses the floor as one side, it often requires fewer materials and can be more compact than other designs.
- It’s particularly effective for tasks where objects are primarily on the ground.
- Disadvantages:
- It’s less effective at capturing objects not on the floor or at varying heights.
- The robot often needs to approach objects more head-on compared to horizontal rollers, which might require more precise driving or programming.
- Advantages:
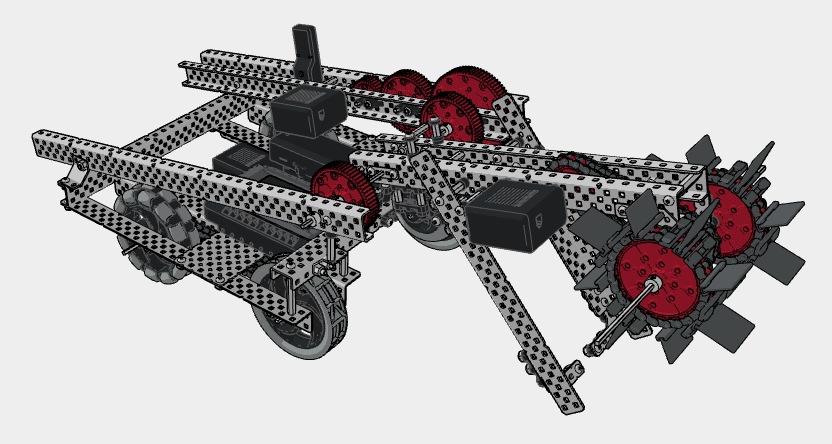
Below is an example from the 2023-2024 VRC game Over Under, Hero Bot Striker. You’ll usually find the vertical roller in front of the robot which uses two rotating sprockets with chains and traction links / rubber flaps which employ the “slapping” mechanism to intake objects.
- Continuous Roller Intake
- Advantages:
- Maintains constant contact with objects, which can be especially useful for tasks that require manipulation over longer distances or durations.
- Objects can be moved at various speeds or even paused in place, giving flexibility in object manipulation.
- Disadvantages:
- If objects are not perfectly aligned or if there are multiple objects, the mechanism might jam.
- Takes longer to assemble and requires more intricate components compared to the previously mentioned intake mechanisms.
- Advantages:
Below is an example of a continuous roller intake using IQ components. Note that the determining factor in building a continuous roller is the near constant contact with the game object, by the intake. A similar mechanism can be built in V5 by simply using chains and traction links.
By understanding the strengths and limitations of each intake mechanism, roboticists can tailor their designs to best meet the challenges they face. Whatever the task, there’s likely an intake design suited for it. What intake mechanisms have you experimented with?