2022-2023 VEX IQ Competition (VIQC) is coming. Are you ready to play the exciting VIQC Virtual Skills game?
To complete the challenge tasks effectively, localization and efficient navigation are two of the key components. This post will focus on the localization.
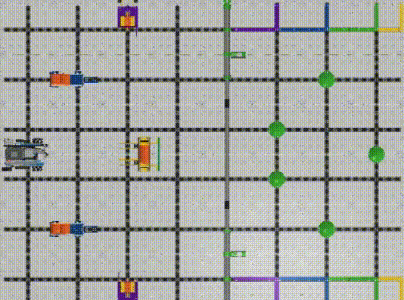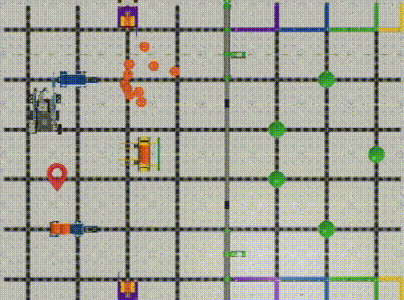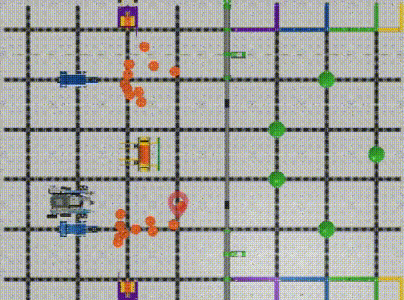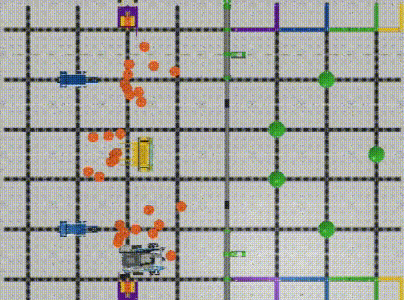
When we start to do a task, we need to drive the robot to a specific position. (Image 1) To perform successful navigation, it is important for us to figure out the robot’s current position and target position.
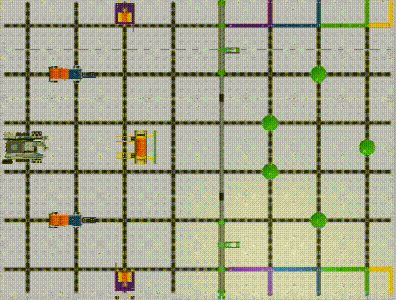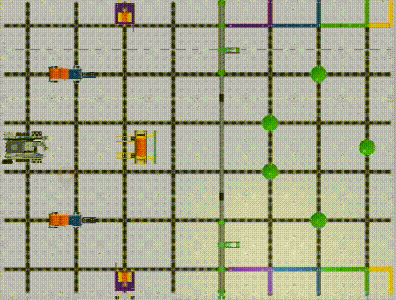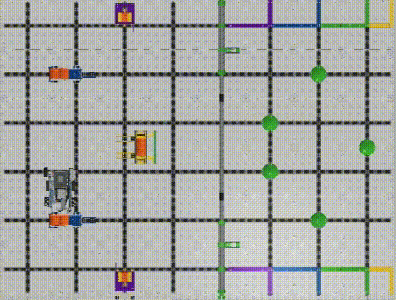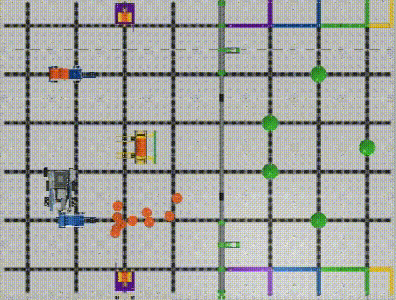
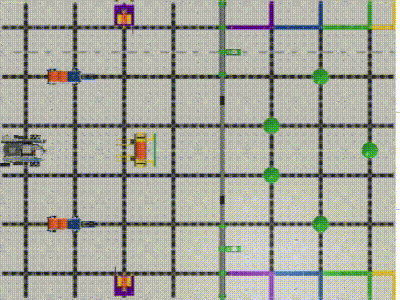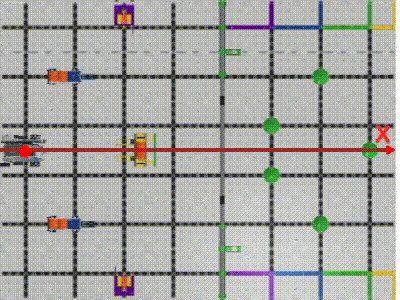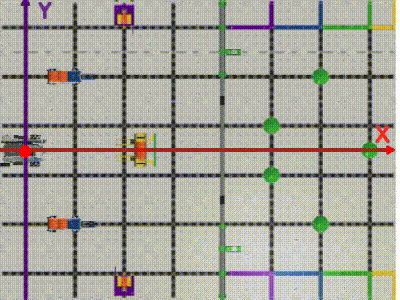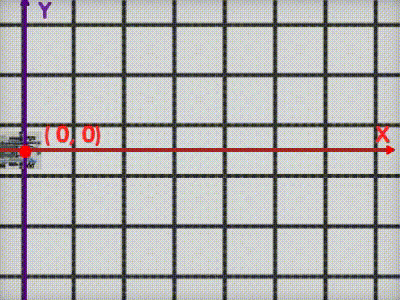
VEX IQ Virtual Skills Field provides us with precise dimensions and setup information. We can create a coordinate system on this map with the robot’s initial position as the origin(0,0). (Image 2)
We can implement the relative localization, evaluating the robot’s position and heading using the information provided by the drivetrain sensing.
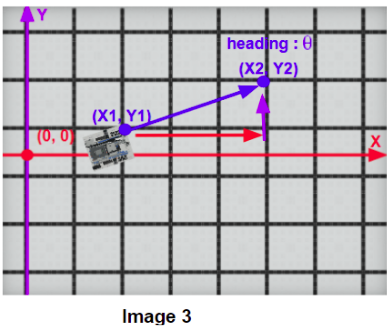
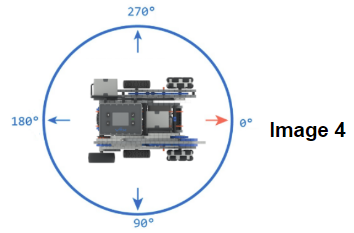
The robot’s X and Y displacement can be calculated utilizing its moving distance and heading angle. (Image 3, Image 4) With the robot’s previous position, we can figure out its current X, and Y coordinates after the movement. (Please see the Example Formula)

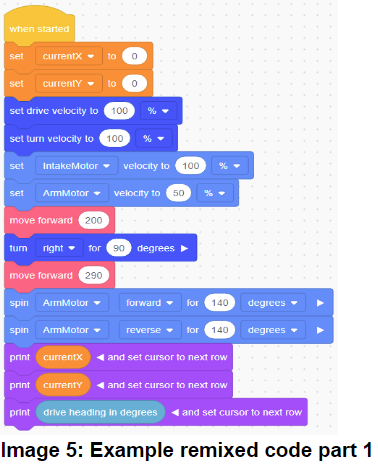
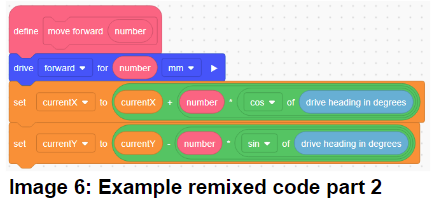
Hence, we can design an algorithm and remix the example code to find out the coordinates of the positions for the robot to complete each task. (Image 5, 6, 7)Remember, the angle used in the algorithm is the heading angle not the quadrantal angles.

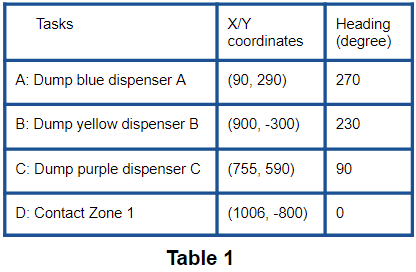
Here are the example positions and heading value for the robot to complete the tasks.
The positions and heading data in Table 1 are recorded from the VCIQ Visual Skills Example codes. When using different solutions, the value will change. We can always record the data of various solutions for future use.
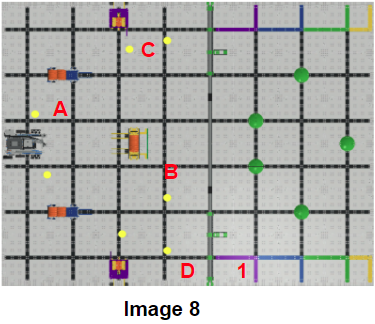
After identifying the specific positions for the game(Image 8), we can start to plan the necessary steps to complete the tasks and score the points as much as possible, and utilize the position and heading value to drive the robot from its current position to a specific position. (Image 9) Please let us know if you have any questions, comments, or feedback. Thank you!